The three steps it takes to solve each circuit are essentially the following:
Finally it is helpful to think about V,R and I, at various points in the circuit, in terms of ratios. That will be clear in the solutions that follow.
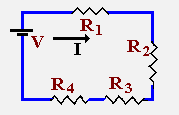
Circuit 1:

Information Given:
Determine values for the remaining R's and determine the total current I.
Steps:
V = V1 + V2 + V3 =20 R = R1 + R2 + R3 =20 Therefore I = 1 (everywhere in this circuit)
 Begin by writing down all you know:
Begin by writing down all you know:
Circuit 2:
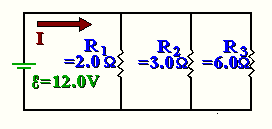
First thing to notice: this is a parallel circuit. So that means
First you need to determine total R using the resistance
in parallel rule:
I1 = V/R1 = 12/2 = 6
Notice of course that I1 + I2 + I3 = I = 12
as it is supposed to.
I2 = V/R2 = 12/3 = 4
I3 = V/R3 = 12/6 = 2
Circuit 3:
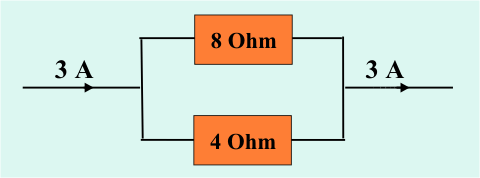
Anal way:
What is total resistance:
1/R = 1/8 + 1/4 = 3/8; R = 8/3
I = 3
V = I*R = 3*8/3 so V = 8
Top resistor: V=R*I; 8=8*I; I = 1
Bottom resistor: V=R*I 8 =4*I; I = 2
Better way;
Notice the ratio of the resistors is 2:1; therefore the ratio of the currents is 1:2; that is Itop = 1 and Ibottom = 2.
Circuit 4:
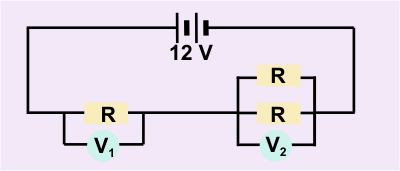
This is not a strictly parallel circuit. It is a series circuit with two parts: A parallel resistance at location 2 and a series
resistance at location 1. The individual R values for each resistor are
identical and it matters not what the actual value of R is.
So, for simplicity let R = 1.
The total resistance of the parallel part is 1/R = 1/1 + 1/1 = 2
so R = 1/2.
The series resistance is clearly R = 1.
The same amount of current must flow through position 2 as position 1.
The resistance at position 2 is 1/2 as much as the resistance at position
1. Therefore it takes 1/2 as much Voltage to push that current through
position 2 as position 1.
Hence V1 = 2*V2 and you also know that
V1 + V2 = 12
Therefore V1 =8 and V2 = 4.
Circuit 5:
1/R = 1/4 + 1/8 = 3/8 so R = 8/3
total resistance is 4 in the series part.
Total resistance in the parallel part is:
1/R = 1/4 + 1/4 = 1/2 so R = 2
For the complete circuit total R = 4+2 = 6
1/R = 1/4 + 1/4 + 1/4 = 3/4 so R = 4/3