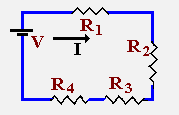

Determine values for the remaining R's and what the total current I is.
 Well begin by writing down all you know:
Well begin by writing down all you know:
Circuit 2:
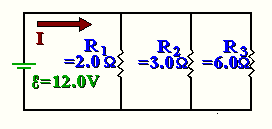
1/R = 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/6 = 1/1; R =1
Apply ohms law to total circuit: V = 12 = R(=1) * I; so I = 12 Now apply ohms law to each resistor:
I1 = V/R1 = 12/2 = 6
I2 = V/R2 = 12/3 = 4
I3 = V/R3 = 12/6 = 2
Circuit 3:
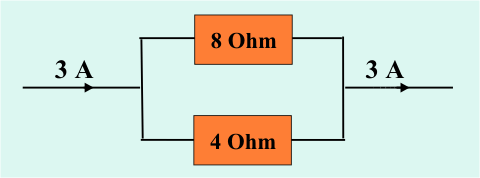
Two ways to work this out:
Anal way:
What is total resistance:
1/R = 1/8 + 1/4 = 3/8; R = 8/3
I = 3
V = I*R = 3*8/3 so V = 8
Top resistor: V=R*I; 8=8*I; I = 1
Bottom resistor: V=R*I 8 =4*I; I = 2
Better way;
Notice the ratio of the resistors is 2:1; therefore the ratio of the currents is 1:2
Circuit 4:
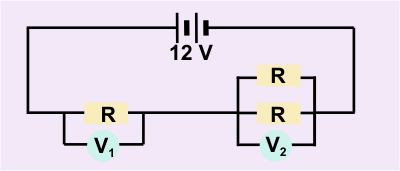
The resistance of the parallel part (at location V2) is:
1/R= 1/2+1/2 =1; R=1
the resistance at location V1 is obviously = 2 so the
total resistance is 1 +2 = 3 ohms. Total current is then 12/3 = 4 amps.
Too find the voltage drops, now treat this as a serial circuit with
equivalent resistance of 2+1 ohms.
So V1 = 2x4 = 8 Volts
V2 = 1x4 = 4 Volts
Note that it doesn't matter what the value of R actually is, the same
values of V1 and V2 are always found.
Ratio way
In series circuit I is constant; V=RI; If R goes up; V goes up;
Ratio of R's is 2:1 therefore ratio of V's is 2:1 or 8 volts at
position 1 and 4 volts at position 2.
1/R = 1/4 + 1/8 = 3/8 so R = 8/3
1/R = 1/4 + 1/4 + 1/4 = 3/4 so R = 4/3