Energy Storage
Why is Energy Storage Important:?
- It's what is required to make low duty cycle alternative
energy sources viable
 especially solar. Need to store the
excess energy when the collector system is being irradiated especially solar. Need to store the
excess energy when the collector system is being irradiated
- Energy storage is also important for power leveling for
the power companies
 Generating stations operate more efficiently
if they run at constant output level Generating stations operate more efficiently
if they run at constant output level  want to shove unused
energy to a storage system and recover it later at times of peak
demand. want to shove unused
energy to a storage system and recover it later at times of peak
demand.
- Energy storage must consider both the amount of energy that can be
stored (energy density of the material) and the efficiency at which it
can be recovered. Some materials have high energy storage capacity but
low rate of recovery.
Energy Density of Some Materials (KWH/kg)
Hydrogen ------------------------- 38
Gasoline ------------------------ 38
Gasoline ------------------------ 14
Lead Acid Batteries -------------- 14
Lead Acid Batteries -------------- 0.04
Lithium Ion Batteries ------------ 0.04
Lithium Ion Batteries ------------ 0.15
Flywheel, Steel ------------------ 0.15
Flywheel, Steel ------------------ 0.05
Flywheel, Carbon Fiber ----------- 0.05
Flywheel, Carbon Fiber ----------- 0.2
Flywheel, Fused Silica ----------- 0.2
Flywheel, Fused Silica ----------- 0.9 0.9
Energy density storage drives the choices that can be made and
is essentially a tradeoff between stored power density and stored
energy density.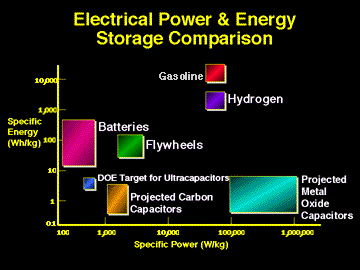
Power = energy x time of usage
so systems with large power densities but
small energy densities means that they discharge their power
relatively quickly. Systems with large stored energy densities
generally mean systems that discharge power at relatively slow rates.
Only gasoline and hydrogen have both high power and high energy storage
capacity. Batteries have good power storage but they tend to discharge pretty fast which compromises their energy storage.
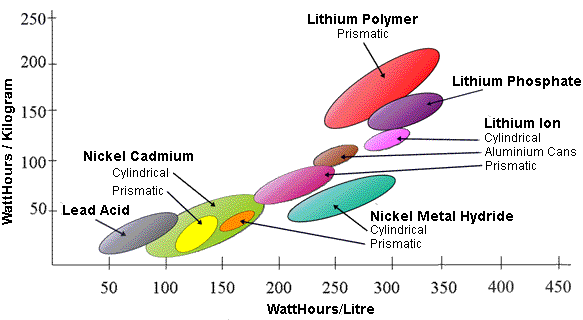
Industry goal is to reach at least 400 watt hours per kg on a production scale -
Envia Systems
But as of Dec 2013 Envia Systems is no more and this is a major setback. But They may be back now . In
addition, the The Battery 500 Project is now real
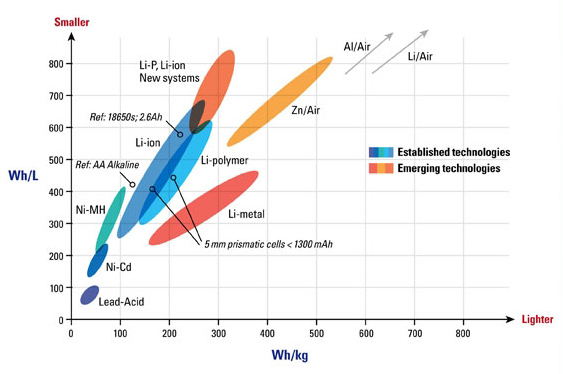
The global race to build a better battery - the search for the right material:
New form factor - Lithium Polymer (LiPO) - has emerged and these can have energy densities as high as 250 watt hours per kg.
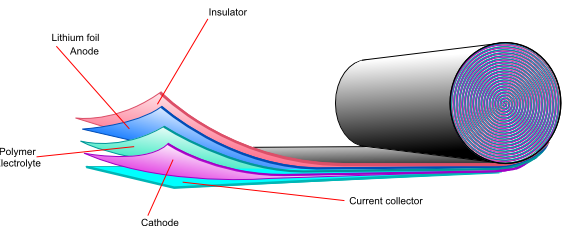
Figure of Merit for "practical EVs":
A driving range of 300 miles requires about 400 KWH of storage
energy (e.g. 10 gallons of gas).
At energy density of 150 watt hrs per kg it would require 2666 kg of
batteries to store 400 KHW of energy - this is more than the weight of the vehicle. This is the basic
problem with current battery technology and current vehicle design.
Now let's suppose one has a lightweight vehicle that could get 60 mpg
(like the Insight does).
At 60 mpg one would use about 5 gallons to go 300 miles and that's equivalent
to about 200 KWHs of storage.
With a battery material that could get 500 watt hours per kg, then you
would need a mere 400 kg to cover this range. Those technologies would
make pure electric vehicles feasible. We are not there yet (or even
close).
Who killed the electric vehicle  Poor energy density
storage of batteries! Physics, not conspiracies. Poor energy density
storage of batteries! Physics, not conspiracies.
Read This: Material in it will be on the Quiz:
More on Batteries Good overview of
different types; advantages and dis-advantages and the like. Read this
resource in detail especially the section related to Annode and Cathode materials. This is one area of Research the the Knight Campus needs to invest in!
Flow Batteries:
Excitement over flow batteries derives from their attributes, which combine aspects of conventional batteries and fuel cells. They are relatively
simple, efficient, scalable, durable, and can optimize either power or energy output, as desired. Flow batteries can respond in fractions of a second and can cycle rapidly and deeply at high or low power output with minimal battery degradation.
Flow batteries are scalable from a few watts and kilowatt-hours to tens or hundreds of megawatts and megawatt-hours.
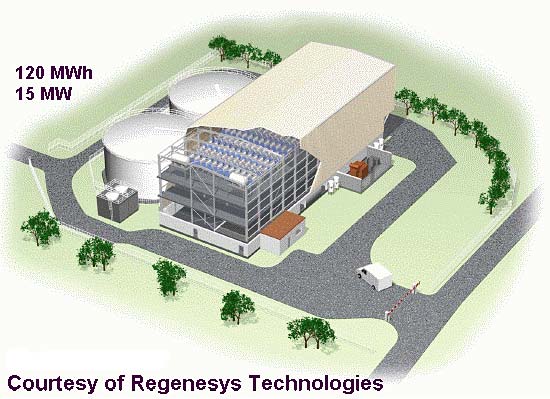
The Turlock Project
1 MW Iron-Chromium (ICB) Flow Battery
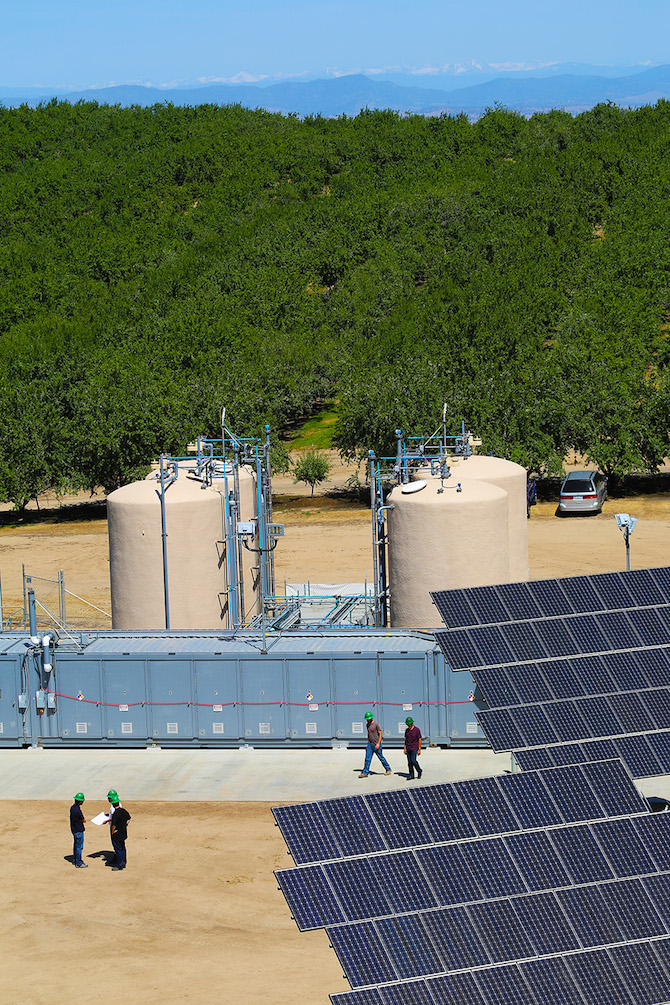

The concept of using large flow batteries at Wind Farms, which you would
think would be a no-brainer, has finally started to catch on. Duh!
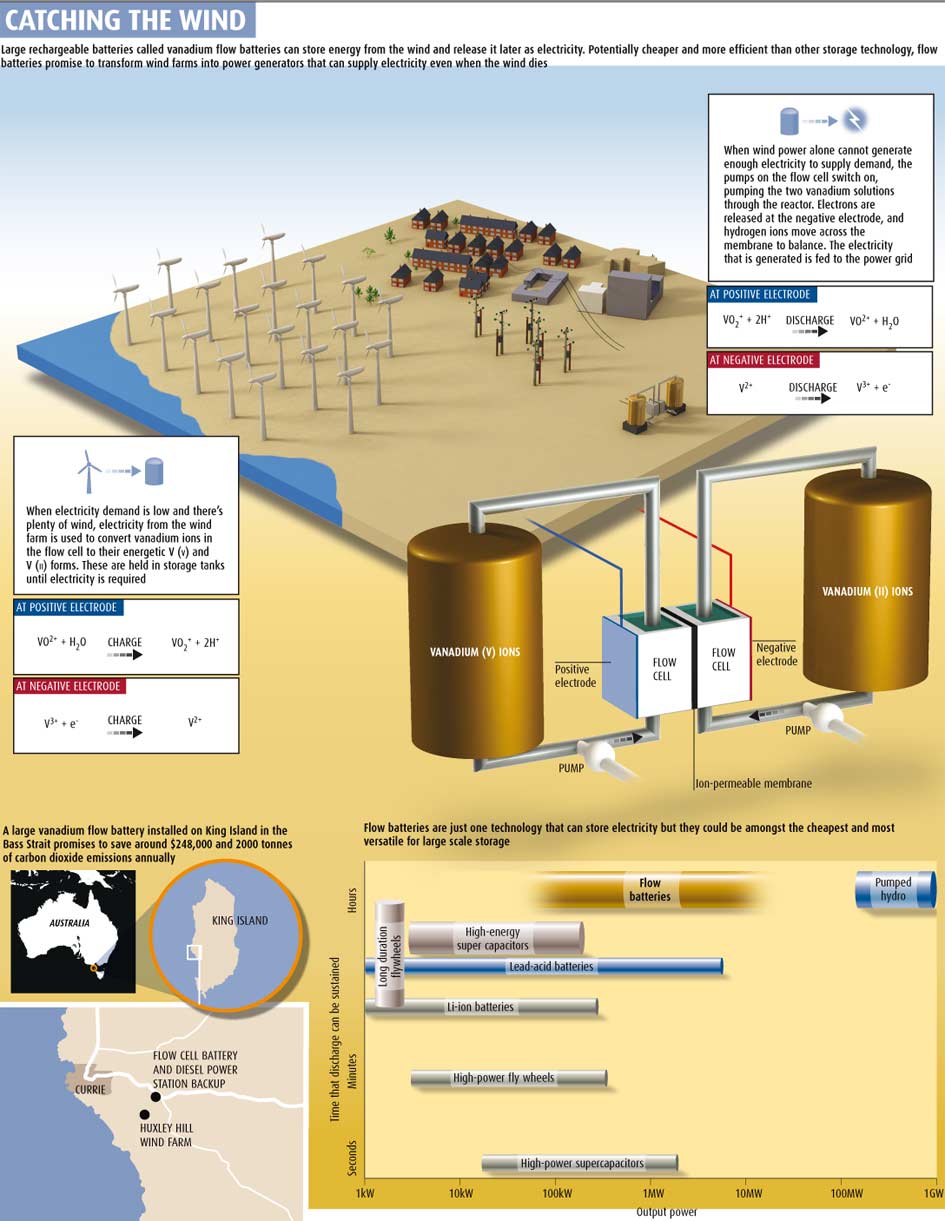
Alas the expansion of this project from a 2.5 MW wind farm to a 600 MW wind farm, however, has now been scrapped
but some wind+storage facilities do exist
|
 especially solar. Need to store the
excess energy when the collector system is being irradiated
especially solar. Need to store the
excess energy when the collector system is being irradiated
 Generating stations operate more efficiently
if they run at constant output level
Generating stations operate more efficiently
if they run at constant output level  want to shove unused
energy to a storage system and recover it later at times of peak
demand.
want to shove unused
energy to a storage system and recover it later at times of peak
demand.




 38
Gasoline ------------------------
38
Gasoline ------------------------ 14
Lead Acid Batteries --------------
14
Lead Acid Batteries -------------- 0.04
Lithium Ion Batteries ------------
0.04
Lithium Ion Batteries ------------ 0.15
Flywheel, Steel ------------------
0.15
Flywheel, Steel ------------------ 0.05
Flywheel, Carbon Fiber -----------
0.05
Flywheel, Carbon Fiber ----------- 0.2
Flywheel, Fused Silica -----------
0.2
Flywheel, Fused Silica ----------- 0.9
0.9

 Poor energy density
storage of batteries! Physics, not conspiracies.
Poor energy density
storage of batteries! Physics, not conspiracies.
