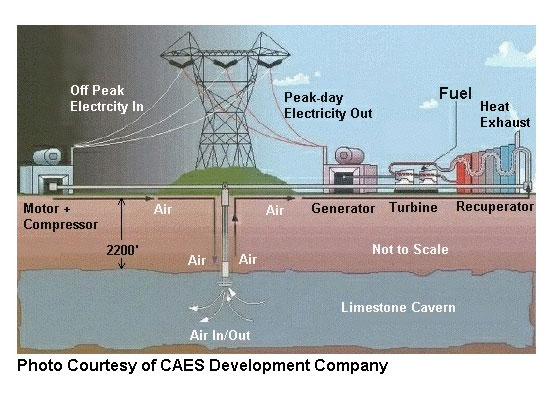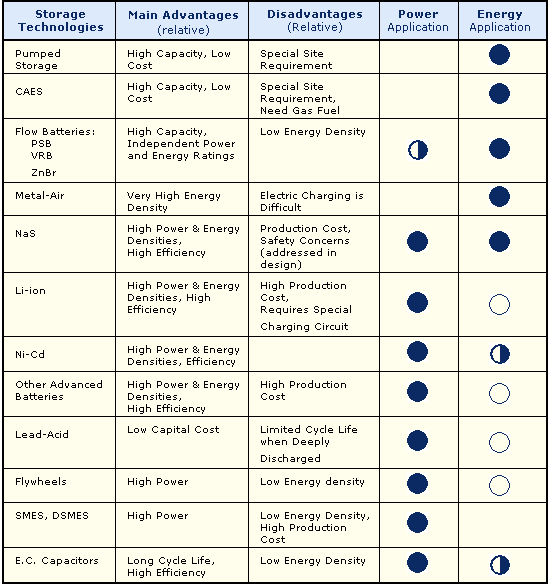
Impact Energy Storage and Snake Charming (this is a serious concept)
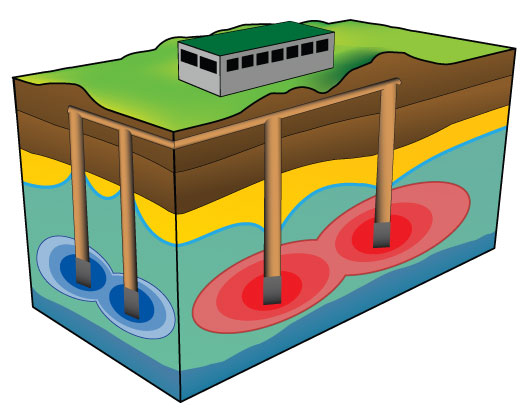
Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage (ATES)

The next step beyond this is the borehole system where many holes are drilled to tap warm groundwater. A working example is the Univeristy of Ontario Institute of Technology
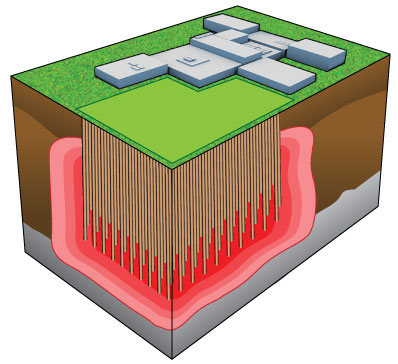
Similiarly, rooftop systems are easy to install tho there are load bearing issues:

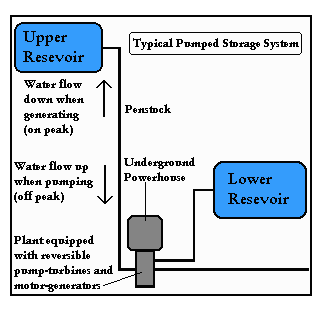

 use excess energy to pump water uphill
use excess energy to pump water uphill
 pump from lower reservoir (natural or artifical) to upper
reservoir.
pump from lower reservoir (natural or artifical) to upper
reservoir.
Energy recovery depends on total volume of water and its height above the turbine
 this is a stringent limit
on locations
this is a stringent limit
on locations
 can achieve higher energy density due to large vertical distance
(up to 1000 feet!)
can achieve higher energy density due to large vertical distance
(up to 1000 feet!)
Cost Issues:
Suppose a company has a coal fired plant which operates at 36% efficiency and uses excess power to pump water uphill. The overall efficiency of recovering that to deliver to the consumer is 0.36 x 0.64 = 0.23 (23%)
 what's the incentive?
what's the incentive?
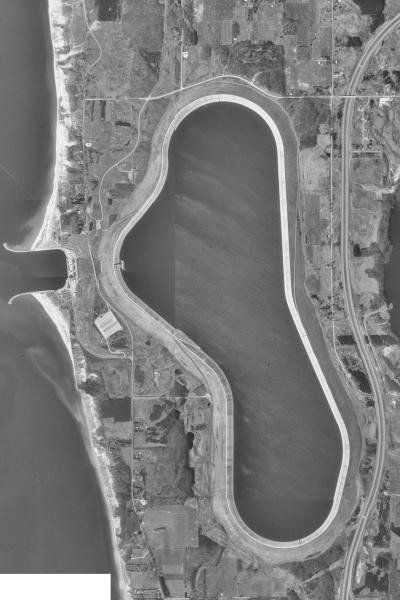
Real Life Facility in Michigan

China now has the largest facility in Asia:
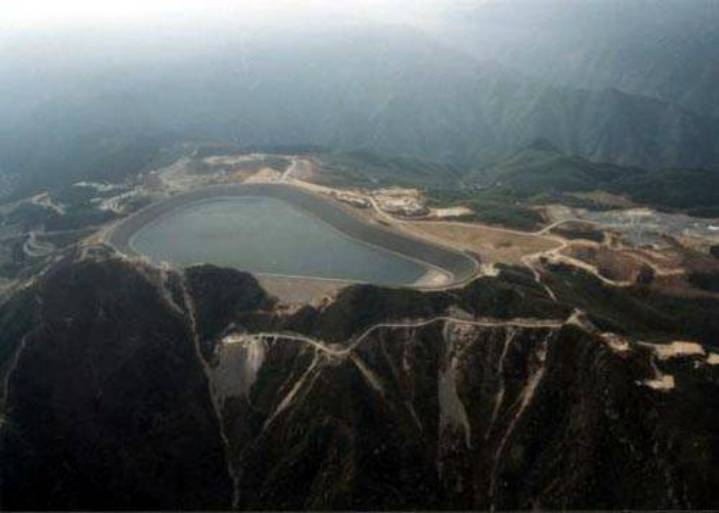

Specifications:
Also the world's first seawater pumped storage facilty recently came on line. Height is 600 m above sea level; total capacity is 600 MW.

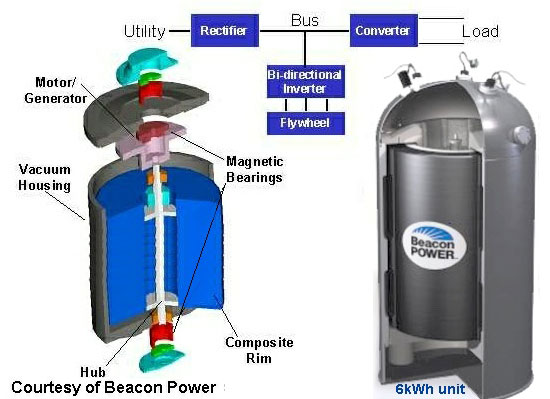
A flywheel, in essence is a mechanical battery - simply a mass rotating about an axis. Flywheels store energy mechanically in the form of kinetic energy. They take an electrical input to accelerate the rotor up to speed by using the built-in motor, and return the electrical energy by using this same motor as a generator.Flywheels are one of the most promising technologies for replacing conventional lead acid batteries as energy storage systems.
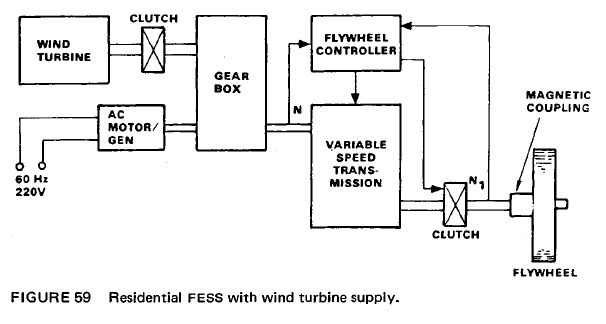
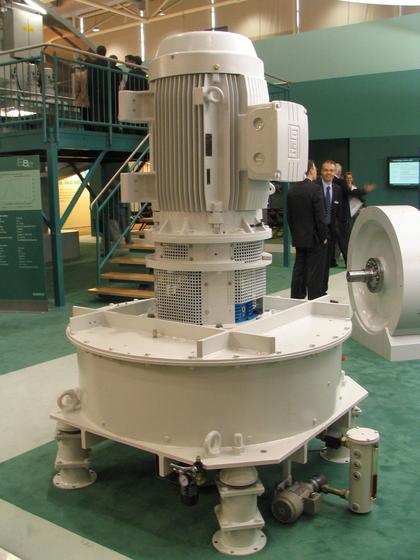 For off grid systems with wind energy, the flywheel storage equilibrates the continual fluctuations of the wind energy. 5 kWh storage capacity and 200kW peak power for 90 seconds.
The Enercon flywheel storage runs in vacuum. About every 5 years, the bearings have to be replaced.
For off grid systems with wind energy, the flywheel storage equilibrates the continual fluctuations of the wind energy. 5 kWh storage capacity and 200kW peak power for 90 seconds.
The Enercon flywheel storage runs in vacuum. About every 5 years, the bearings have to be replaced.
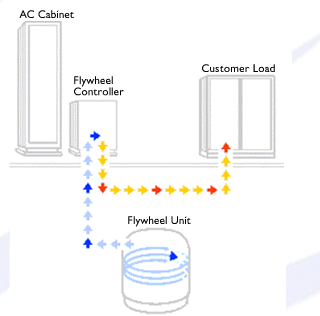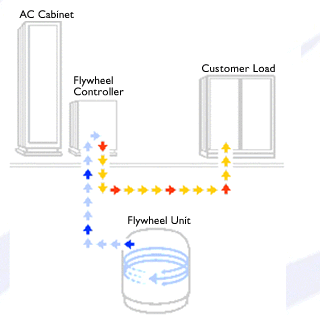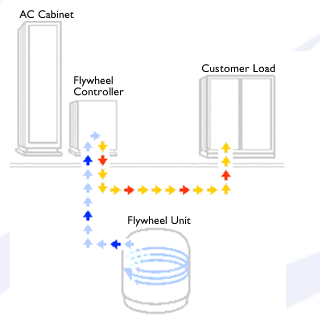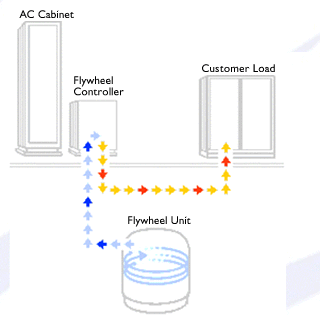
So, in other words. During times that your
generating more power than you need, you can spin the fly wheel up,
so to speak. When you need to recover that energy, you let the fly wheel
spin down.
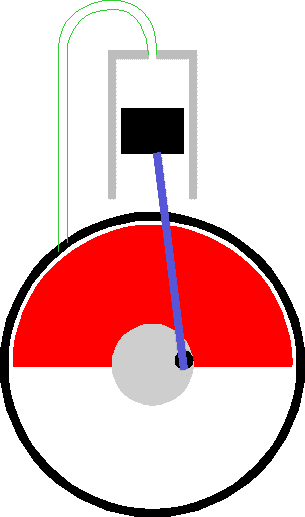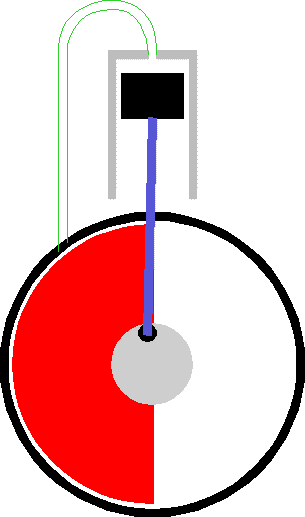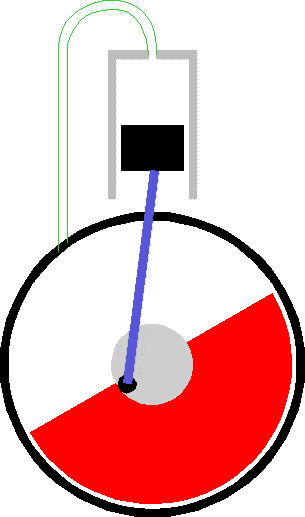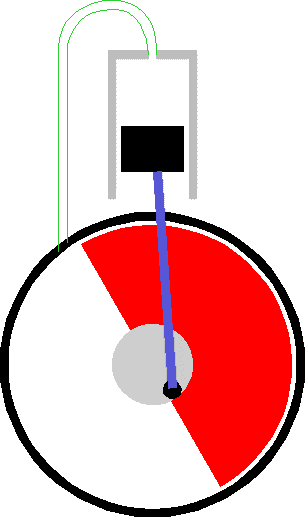
To optimize the energy-to-mass ratio the flywheel needs to spin at the maximum possible speed. This is because kinetic energy only increases linerarly with Mass but goes as the square of the rotation speed.
Rapidly rotating objects are subject to centrifugal forces that can rip them apart. Thus, while dense material can store more energy it is also subject to higher centrifugal force and thus fails at lower rotation speeds than low density material.
Tensile Strength is More important than density of material.
Long rundown times are also required  frictionless bearings and
a vacuum to minimize air resistance can result in rundown times of
6 months
frictionless bearings and
a vacuum to minimize air resistance can result in rundown times of
6 months  steady supply of energy
steady supply of energy
Flywheels are about 80% efficient (like hydro)
Flywheels do take up much less land than pumped hydro systems
Fused Silica Flywheels are possible:
 High tensile strength material allows it
to be rotated very fast (100,000 rpm) without flying apart
High tensile strength material allows it
to be rotated very fast (100,000 rpm) without flying apart
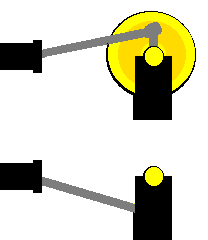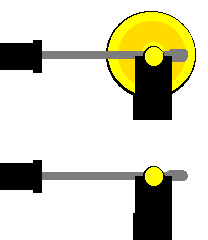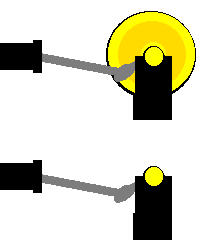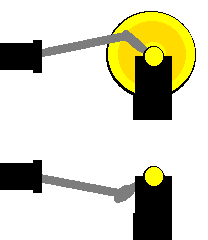
The model with the small yellow disc tends to stop when the crank and connecting rod are in a straight line ('dead' spots) - because sliding the brass knob exerts no turning force on the shaft. In the model with the big yellow flywheel, it is easy to keep the disc turning, once it has started, due to the effect of the flywheel. The mass and the size of the big flywheel helps resist the slowing down of the model as it is turning.
Current Use of Flywheels; Frequency Regulation
Beacon Power - the Leader in Flywheel Technology