Ideally, this is best down using two locations at the same meridian (line of longtitude on the earth).
As latitude is equivalent to declination, then using the difference in shadow lengths at noon will define the angular difference between two locations on the earth.
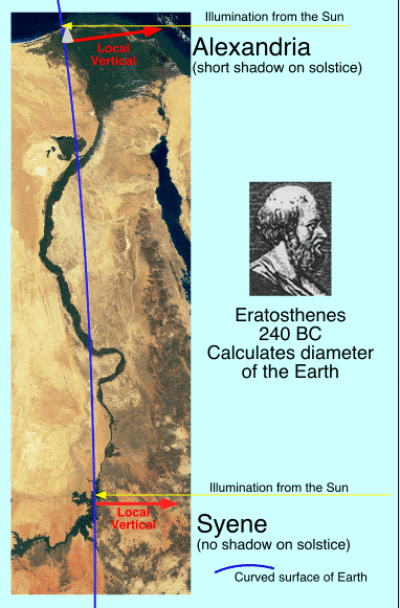
Historically this was done by Eratosthenes using a known location where the sun was directly overhead and cast no shadow and another location where the shadow at that same time was 7.5 degrees. Thus the angular distance between these two locations (syene and alexendria) was 7.5 degrees. If you then walked from syene to alexendria (or took a camel, or whatver) with a tape measure to measure the distance, then you could calculate the radius of the earth using ratios as detailed below.
We can repeat this exercise conceptually, by simply using a GPS unit or equivalently google maps
