Various Environmental Stimuli
for Evolution:
How does intelligence arise?

Or Does it?
Psssive (Millions of years timescale):
Dispersal of Parental Units by a variety of mechanisms:
Passive: (slowly alters gene pool over time)
- Migratory Random Walks
- Continental Drift
- Mountain Building
- Climate Changes (Periodic Ice ages
 this one
is on timescales of 100,000 years recently)
this one
is on timescales of 100,000 years recently)
Active (catastrophe  "overnight" change in ecosystem)
"overnight" change in ecosystem)
- Asteroid Impacts
- Large Floods (from Ice Ages)
- Volcanic eruption
- massive earthquake
- the rapid emergence of 6.5 billion humans
Survival of the fittest works in well-defined, slowly evolving
ecosystems (like the ocean); On long time scales, the role of
random catastrophe is more important
|
Mass Extinctions in Geological History
Startling evidence
for many events

Pay attention to Percent of Species Extincted

Some Evidence for Periodic Extinction Events of varying amplitude

Mass extinctions mean:
- 1/2 to 2/3 of all species (plant and animal) eliminated
- plankton in the ocean is extincted
- both land and water are affected
The evolution of intelligence? The rate of increase of
EL as measured by the fossil record.
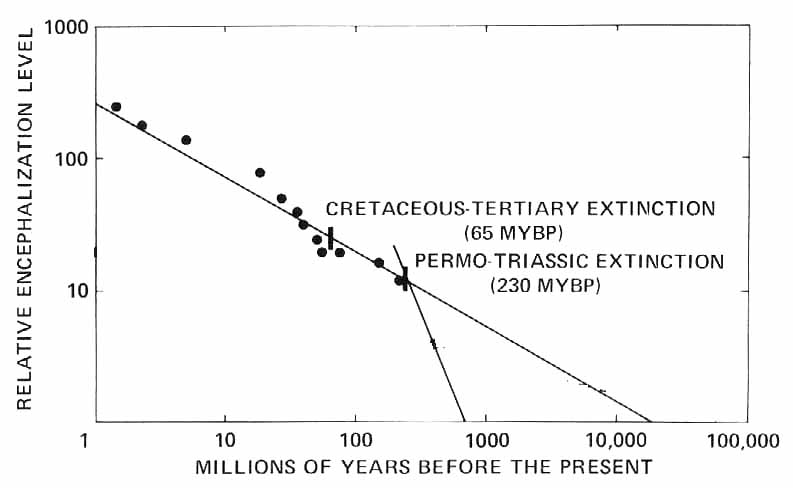
What Can we Conclude from the above
Graph:
- Increase in Relative EL exhibits a well defined pattern
over the last 200 million years
- Fastest growth was from 600--250 million years ago when species
first emerged on the land
- Mass extinctions clearly are important as they substantially
alter the rate of growth
- Unaltered rate would have produced current human level of EL
about 60 million years ago
- Continental rate is much higher than the oceanic rate
- Smooth extrapolation backwards from last few million years of
continental data suggests it takes 20 billion years for intelligence
to emerge
It seems likely than when terrestrial ecosystems developed, the flow
of nutrients to the oceans became impaired which served to suppress
that ecosystems growth rate over the rest of geologic time.


 this one
is on timescales of 100,000 years recently)
this one
is on timescales of 100,000 years recently)
 "overnight" change in ecosystem)
"overnight" change in ecosystem)



